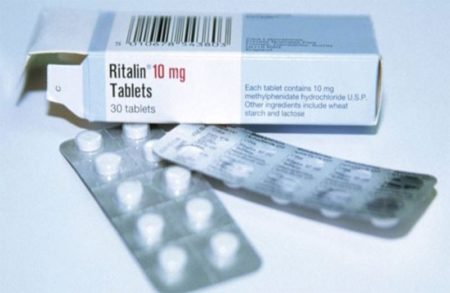
Methylphenidate (Ritalin) is a non-amphetamine-type psychostimulant. The drug is on list 1 of the list of narcotic drugs, psychotropic substances and their precursors to be controlled in Russia, and produces pharmacological effects similar to those of amphetamine and cocaine.
Psychiatrists have been using this drug for over 40 years, they and pharmacologists did not know then, and now do not know how and why it works. Other names of the drug: meridil, centedrine, methylphenidatum, centedrin, rilatine, methylphenidati hydrochloridum, methylphenidate hydrochloride.
History:
The drug was synthesized in 1944. In 1961, doctors from different cities of the United States drew attention to the fact that new-generation drugs of the CNS stimulant group methylphenidate and dextroamphetamine help children with attention deficit hyperactive disorder (GDVD), but they are much less likely to cause side effects compared to benzedrine. After that, the company “Ciba-Geigy” proposed the use of Ritalin (methylphenidate) for the treatment of this disease. The drug was initially rejected by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), but was then approved for such a testimony in 1963.
According to the US Drug Enforcement Administration, street abuse of methylphenidate has become a serious problem. Introduced into American schools in the 1960s, now this drug costs drug dealers $ 10 to $ 15 per dose, although the production of this substance in clandestine laboratories is not fixed. The United States consumes 85% of total methylphenidate (Ritalin) production.
In 2002, the Parliamentary Assembly of the Council of Europe noted the high level of legal consumption of methylphenidate in Belgium, Germany, Iceland, Luxembourg, the Netherlands, Switzerland and the United Kingdom. The number of British children who are prescribed stimulants has increased by 9,200% between 1992 and 2000, while in Australia the number of prescription stimulants for children has increased 34 times over the past 20 years. In France, from 1989 to 2002, the number of children diagnosed with hyperactivity increased by 600%. In Mexico, methylphenidate sales jumped 800% from 1993 to 2001.
In medicine:
Methylphenidate (Ritalin) has limited use in medicine as a psychostimulant for asthenic conditions, increased fatigue. It can be used for inhibition of the nervous system caused by antipsychotic drugs, narcolepsy. It is also prescribed for the treatment of attention deficit disorder, activity disorder, depression.
Act:
According to the action, methylphenidate (Ritalin) is similar to amphetamine, but it has a less strong stimulating effect and less affects the peripheral adrenergic systems; a marked increase in blood pressure does not cause. It suppresses appetite, causes wakefulness, increases concentration and attentiveness, euphoria.
Pharmaceutical tablets are most often taken orally or they are crushed and sniffed in powder form. However, some drug addicts dissolve the tablets in water and inject the liquid inside.
Side effects are possible: nausea, insomnia, sometimes anxiety and agitation, exacerbation of psychopathological symptoms, can be addictive.

Danger:
Complications arising from the use of ritalin (methylphenidate) are caused by insoluble excipients used in tablets. When administered, these materials block small blood vessels, causing serious damage to the lungs and retina. Methylphenidate also produces an increase in heart rate and blood pressure as a result of taking large doses, and can lead to serious psychological dependence.
Recently, the use of Ritalin (methylphenidate) has become widespread – students began to consume it widely, according to which this helps to focus attention during the pre-examination preparation. What may be the long-term effect of such an initiative is still unknown.